[vc_row alt_color=”” alt_bg_color=”” parallax=”” full_width=”” full_screen=”” background_overlay=”” mask=”” mask_style=”50″ vertical_align=”” padding_size=”” el_class=””][vc_column alt_color=”” alt_bg_color=”” text_align=”” padding_size=”” el_class=”” width=”1/1″][vc_column_text]Whiplash injury and automobile accidents
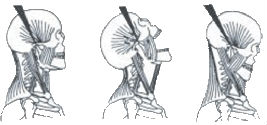
Whiplash typically occurs when the head is thrown backward and forward while riding in a car that is hit from behind or the side. Extensive research shows that most flexion-extension injuries occur following what is called “minor head injuries.” This means that it is not necessary to suffer a fracture or even a direct head impact. In fact, most patients report that their head was simply snapped backward and forward or side-to-side. This motion causes damage to the muscles and ligaments, which support the jaw joint. When these muscles and ligaments are injured, this can cause an anterior displacement of the protective disc and result in a dislocated jaw joint on one or both sides..
Intubation procedures in hospitals
Patients that undergo surgical procedures with general anesthetic are usually intubated through the mouth. Intubation involves placing a tube down the throat to keep the airway open during surgical procedures. Occasionally, the jaw can be dislocated during this procedure due to the forced opening of the mouth and the hyperextension of the ligaments and tissues while inserting the tube. Some patients may experience clicking in the jaw, limited opening of the mouth, facial pain, and headaches post surgically. Those patients who have already been diagnosed with a TM disorder should advise the anesthesiologist that they wish to be intubated through the nose during any surgical procedure to prevent further damage to the joint and its surrounding structures.
Trauma to the head, face or jaw A severe blow to the head or to the jaw can cause the disc to be dislocated due to the force of the impact. Patients may experience swelling, limited opening and clicking in the joint. Patients with this acute injury should seek emergency treatment immediately to avoid further damage to the joint.
Regardless of the type of trauma sustained, the temporomandibular joint is affected like no other joint in the body. Behind the condyle, there are several structures that affect the health of the jaw joint itself. One is the posterior ligament, which acts as a rubber band to pull the disc backward during closing of the jaw. Like all joints, the TM joints contain a large amount of nerves and blood vessels which, on a subconscious level give the brain information about the position and condition of the joint. When the mouth is closed, the disc, which has no feeling, acts as a shock absorber to prevent the nerves and blood vessels from being compressed. When the mouth opens and the condyle and the disc move forward, the blood vessels expand to fill the vacated space. When the condyle is pushed too far backwards in the joint, it can slip off the cartilage disc and impinge onto these nerves and blood vessels. Once these are compressed, the whole structure is unbalanced, affecting the nerves, the ligaments and the muscles of the head, neck and face. This dislocated jaw causes pain and other symptoms affecting a person’s health and quality of life.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
